Overview
Memes, as an integral part of internet culture, combine images with brief text to convey humor, opinions, and social commentary. However, memes can also be used to spread harmful content such as hate speech and misinformation. Therefore, developing effective systems to detect harmful memes is crucial for maintaining a healthy online environment.
The paper "MemeBlip2: A Novel Light Weight Multimodal System to Detect Harmful Memes" proposes a lightweight multimodal system that detects harmful memes by jointly modeling visual and textual signals. This method integrates the BLIP-2 vision-language encoder, extending previous research and achieving excellent performance on the PrideMM dataset.

Figure 1: MemeBlip2 System Architecture (Based on BLIP-2)
Paper: MemeBlip2: A Novel Light Weight Multimodal System to Detect Harmful Memes
Background and Motivation
With the rapid development of social media and online platforms, memes have become an important carrier for information dissemination. However, the multimodal nature of memes (image + text) makes their understanding complex, especially when involving sarcasm, specific cultural references, or implicit harmful information. Traditional unimodal detection methods often fail to capture these subtle cross-modal cues.
Although existing multimodal methods can process both images and text, they often face the following problems:
- High Model Complexity: Many existing methods require substantial computational resources
- Insufficient Cross-modal Understanding: Difficulty in capturing deep semantic associations between images and text
- Limited Recognition of Sarcasm and Cultural References
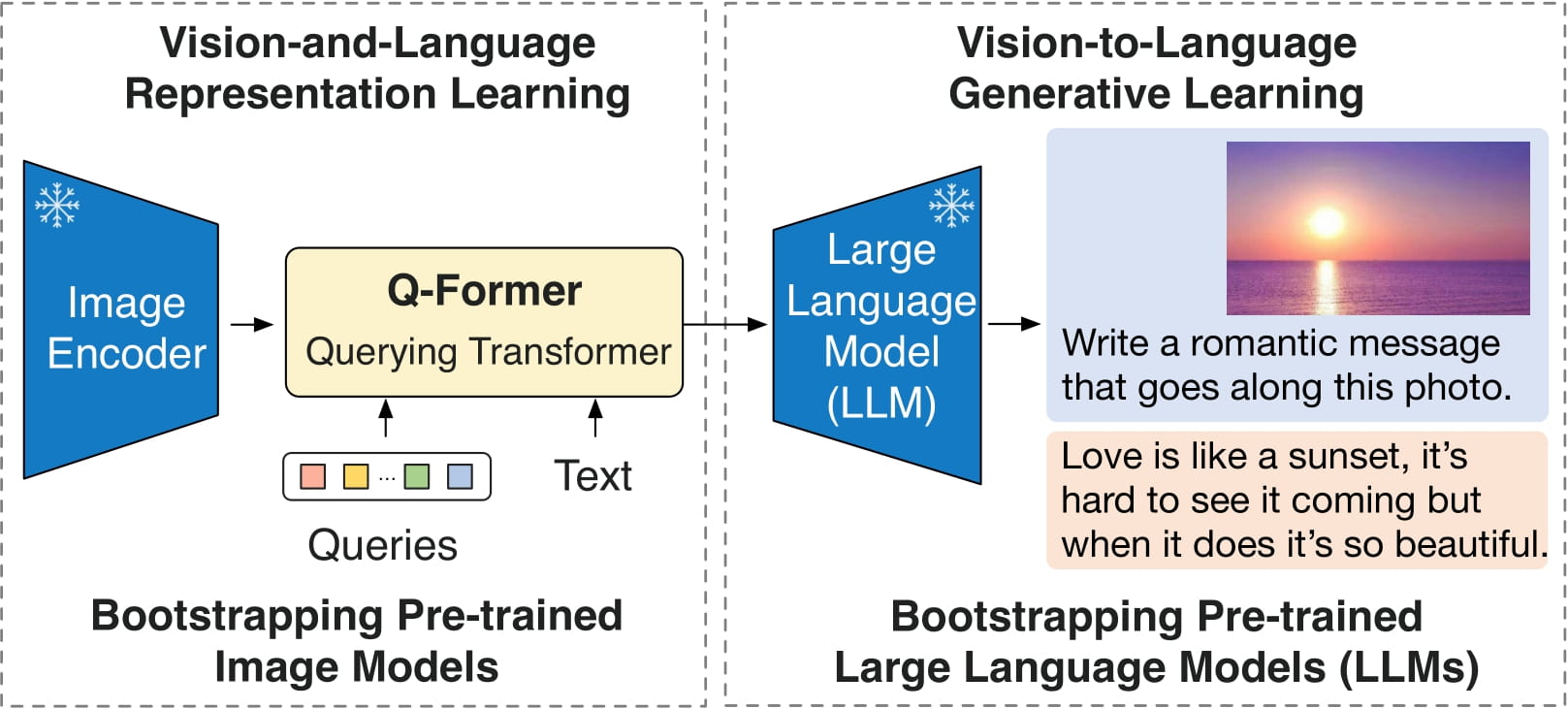
Figure 2: Example of Multimodal Meme Detection Challenge
Core Innovations of MemeBlip2
1. Lightweight Architecture Design
MemeBlip2 adopts a lightweight architecture design that significantly reduces computational complexity while maintaining high performance. This enables the system to be deployed in resource-constrained environments, improving the feasibility of practical applications.
2. BLIP-2 Encoder Integration
The core innovation of the paper lies in integrating the BLIP-2 vision-language encoder. BLIP-2 (Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training 2) is a powerful multimodal pre-trained model that effectively understands the relationships between images and text. By leveraging BLIP-2's pre-trained knowledge, MemeBlip2 can better understand visual-text interactions in memes.
The advantages of BLIP-2 include:
- Strong vision-language alignment capabilities
- Rich pre-trained knowledge
- Efficient cross-modal feature extraction

Figure 3: BLIP-2 Encoder Integration in MemeBlip2
3. Joint Multimodal Modeling
MemeBlip2 captures subtle cues that unimodal methods cannot identify by jointly modeling visual and textual signals. This joint modeling approach is particularly suitable for handling:
- Sarcastic Content: Images and text may express opposite meanings
- Specific Cultural References: Require combining visual and textual context to understand
- Implicit Harmful Information: Conveyed through the combination of images and text
Experimental Results and Performance Analysis
Evaluation on the PrideMM dataset shows that MemeBlip2 achieves excellent performance:
- Accuracy: 77.5%
- AUROC: 81.8%
- Macro F1 Score: 79.0%
These results demonstrate that MemeBlip2 can effectively capture subtle cross-modal cues and outperforms existing multimodal baseline models on this benchmark.

Figure 4: Performance Comparison with Baseline Models (Accuracy: 77.5%, AUROC: 81.8%, Macro F1: 79.0%)
Performance Advantages
The advantages of MemeBlip2 over baseline models are mainly reflected in:
- Better Cross-modal Understanding: Through the BLIP-2 encoder, the system can more accurately understand the relationships between images and text
- Robustness to Complex Scenarios: Better performance when handling complex scenarios such as sarcasm and cultural references
- Lightweight Design: Reduces computational costs while maintaining high performance
Technical Details
Model Architecture
The architecture of MemeBlip2 mainly includes the following components:
- Visual Encoder: Processes input images and extracts visual features
- Text Encoder: Processes text content and extracts textual features
- BLIP-2 Multimodal Encoder: Jointly processes visual and textual information to generate fused multimodal representations
- Classification Head: Performs harmful content classification based on multimodal representations
Training Strategy
The paper adopts the following training strategies to optimize model performance:
- Initialization using BLIP-2's pre-trained weights
- Fine-tuning on the PrideMM dataset
- Multi-task learning strategy that simultaneously optimizes classification and feature learning
Applications and Challenges
Application Prospects
The lightweight design and excellent performance of MemeBlip2 give it broad application prospects in the following scenarios:
- Social Media Content Moderation: Automatically detect and filter harmful memes
- Online Platform Regulation: Help platforms maintain a healthy online environment
- Research Tools: Provide technical support for meme research and online culture analysis
Challenges
Although MemeBlip2 achieves good performance, it still faces some challenges:
- Cross-dataset Generalization: Need to verify the model's generalization ability on different datasets
- Cultural Diversity: Meme understanding may differ across different cultural backgrounds
- Real-time Requirements: Need to meet real-time detection requirements in practical applications
- False Positive Rate Control: Need to avoid misjudging normal content while detecting harmful content
Conclusion and Future Work
MemeBlip2 proposes a lightweight and efficient harmful meme detection system by integrating the BLIP-2 vision-language encoder. Experimental results show that this method achieves excellent performance on the PrideMM dataset and can effectively capture subtle cross-modal cues, including sarcasm and specific cultural references.
Future research directions may include:
- Extending to more datasets to verify the model's generalization ability
- Further optimizing the model architecture to improve performance while maintaining lightweight design
- Exploring more fine-grained harmful content classification (such as hate speech, misinformation, etc.)
- Researching cross-cultural and cross-lingual meme understanding methods
MemeBlip2 provides a promising direction for the field of harmful meme detection, and we look forward to seeing more breakthroughs in practical applications in the future.